HEALTH TECH INNOVATIONS AND ADOPTION IN DEVELOPED COUNTRIES
Like other industries, healthcare is witnessing a shift to consumerization, pushing payers and providers to focus on value-based care and improve the health outcomes. Across various geographies, advanced tools like Artificial Intelligence are being implemented to address varied stakeholders’ challenges and augment care provision.
In most economies, irrespective of the stages of development, the cost and demand for care is rising, thereby increasing the need for digital technologies. It becomes imperative to provide seamless and integrated care by leveraging the benefits of the connected ecosystem, where patients, providers, payers and other stakeholders are increasingly adopting technology to simplify the processes.
Advanced and developed economies like US, Germany, Canada, and UK spend a huge proportion of GDP on healthcare, however, the adoption of proven technologies like AI is yet to gain importance in their health systems. Though the US is the highest spender on healthcare globally, as a percentage of its GDP, it faces challenges like rising cost of healthcare provision, shortage of primary care professionals, poor-quality outcome and lack of coverage for a high percentage of the population. The US spends two and a half times higher than the average of Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) countries on healthcare, with a significant proportion being out of pocket or voluntary coverage. It also has the highest rates of medication errors compared to other OECD countries. The average insurance subscription in the US is about USD 400 a month and a significant amount of healthcare service contributions are co-payments/out of pocket share.
The US market has seen higher adoption of AI in healthcare to decrease the cost of care and improve the outcomes. This was driven by regulatory push for value-based care through various legislations, which forced the providers to adopt Electronic Health Record (EHR) platforms. An (EHR) is an individual's official health document that is shared among multiple facilities and agencies The effective implementation of EHR can act as a foundation for AI to leverage the medical data. Healthcare, compared to other industries, will see a greater potential for AI, addressing many challenges relating to care provision, diagnostics, and drug discovery.
In the US, AI applications and platforms which have been put to practical use, especially in hospital settings, have resulted in tangible benefits. Benefits include early diagnosis of conditions, operational improvements like reduction of wait time and improving care provision workflow, and targeted therapy administration. It is expected that, within the next two years, about 35% of healthcare organizations plan to adopt AI in healthcare to improve patient experience. Arterys, which helps diagnose heart problems in 15 seconds, was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and has since raised USD 28M to speed up global delivery of medical AI . Mayo Clinic collaborated with health tech start-ups like Tempus and AliveCor. Tempus helps Mayo Clinic offer customized treatment options using genomic based therapy to treat conditions like cancer. AliveCor, with its AI platform, helps Mayo Clinic in early detection of Cardiac Arrhythmia. Mayo Clinic recently launched new technology platform ventures to revolutionize diagnostic medicine. Its Remote Diagnostics and Management Platform (RDMP) brings together data and AI algorithms and augments human decision-making within existing clinical workflows.
El Camino Hospital adopted a new technology for fighting cancer resulting in fewer side effects for patients. The technology, Ethos, uses AI to reflect real time anatomical changes for quick adjustments. In the last couple of years, we have seen numerous start-ups entering the healthcare sector to provide AI solutions using their machine learning and big data analytics capabilities, and a number of these startups getting acquired by bigger and more established companies. Google acquired DeepMind in 2014 to compete with major tech companies and gain a stronghold of deep learning in healthcare. Another tech giant, Intel acquired Nervana Systems, a deep learning start-up in 2016. In 2021, Google acquired Fitbit, which allows users to track their health and wellness data, and Microsoft’s acquisition of Nuance which provides conversational AI and cloud-based ambient clinical intelligence for healthcare providers was approved by the European Commission.
AI AND ANALYTICS
Analytics and Artificial Intelligence can go hand in hand to make work simpler and more efficient. Advances in AI have accelerated healthcare transformation, resulting in improved health outcomes whilst reducing the cost of providing healthcare. Analytics relies on combined capabilities of computer programming, statistics and operations research to quantify performance. It is used to interpret large amount of data and draw meaningful conclusions from the available data.
Among the many technology changes over the last decade, data analytics for handling, processing, and gainfully using large amounts of data has seen the most significant growth. However, since data analytics can only work with historical data and give outcomes as predefined by humans, specific rule-based algorithms were developed to augment data analytics, thereby imparting the ‘self-learning’ capability to computers, which is now referred to as “Machine Learning”.
Machine learning did not require the computers to be explicitly programmed, which is a definitive advantage. Machine learning was then combined with data analytics to analyze data and develop complex algorithms to predict models, which was named as predictive analytics. Predictive analytics is driven by a set of rules defined by humans, known as predictive algorithms which are used to analyze historical data to predict future outcomes.
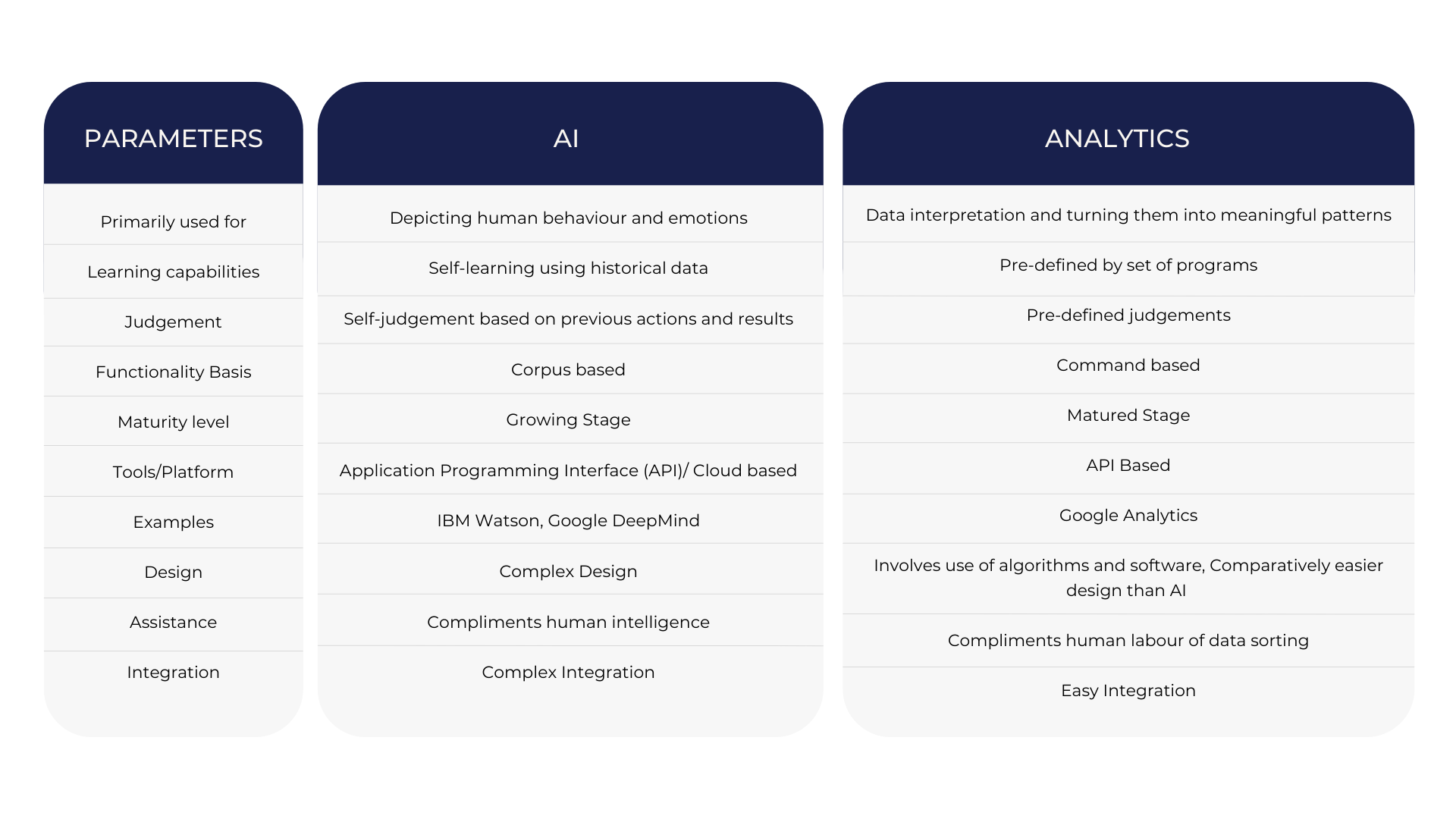
The following table compares AI and Analytics on several parameters:
FOUR AI TECHNOLOGIES TRANSFORMING HEALTHCARE
AI in healthcare is now enabling new possibilities which were assessed as not feasible earlier. IBM’s Watson and Google’s DeepMind are solving real-world problems in medicine, free from cognitive biases, by partnering with various healthcare players.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
AI plays an important role in converting complex data into simple meaningful insights; and this work is made easier by NLP. NLP focuses on mimicking human-like responses, by using algorithms to respond to queries and hold conversations. NLP in the healthcare sector can be used to summarize long narrative text, such as academic journal articles or clinical notes by pointing out the key concepts or phrases in the reference document. NLP can also map data elements in EHRs, which are present as unstructured text, into structured meaningful data to improve clinical decision making.
For example, Intermountain Healthcare used NLP to identify the cause of an illness in a person, by mining medical record data of patients to identify cases like stroke, cancer, heart failure, and cases with venous thromboembolisms (formation of blood clots in the deep veins of the leg).
Deep Learning
The diagnosis and treatment of diseases is likely to further improve with the implementation of AI in the healthcare sector. Deep learning, a component of AI, can be used to analyze medical data and images to enhance the ability of physicians to treat diseases. Deep learning can help the visually challenged make sense of the environment, i.e., AI uses computer vision and text-to-speech to narrate the text, identify facial cues of the people nearby, study the surroundings and describe the environment. Three trends that drive the deep learning revolution include sophisticated neural network algorithms modelled on the human brain, more powerful Graphics Processing Units (GPUs), and access to enormous amounts of data from the internet. For example, IBM Watson is being trained to help doctors with medical diagnosis using cognitive computing and a deep learning approach.
Context Aware Processing
AI can be utilized for virtual assistant applications like Apple’s Siri, Google Assistant, Amazon Alexa and Microsoft Cortana, in the healthcare sector, which can perform tasks as directed by the programmer. AI chatbots, when used in healthcare, can phenomenally reduce the burden on medical professionals to coordinate care and detect issues or diagnosable health concerns. Bots would be an evolution of health assistants. For example, Bots like HealthTap or Your.MD uses AI to find solutions to the most common symptoms. However, chatbots act as enablers in the process to direct the patients to the right physician for diagnosis and therapy. They would supplement the duties of an experienced doctor.
Intelligent Robotics
AI can also be used with robotics. Physical robots can revolutionize life care facilities, by helping people stay healthy and reduce hospitalization needs. AI, coupled with the advanced humanoid design, is powering robots to have conversations and social interactions with aged patients to keep their minds sharp. Since robots have greater flexibility and reach, they can be used for making smaller incisions with more precision in the affected areas. Certain robots can serve as a social partner to treat mental health issues or to alleviate loneliness. Companies such as Blue Frog Robotics (developer of BUDDY), National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, or AIST (developer of PARO), among others have augmented the concept of companion robots in the healthcare sector.
While analytics is based on a predefined set of programs, AI has the capability to self-learn using historical data. When analytics is coupled with AI, it can play a crucial role in data mining of medical records and become an effective platform in the healthcare sector. Along with data mining, analytics can be used with AI to develop predictive models which can help doctors diagnose diseases at an early stage. In order to achieve the above outcomes, analytics and AI need to work in conjunction, which would not only improve but revolutionize the healthcare sector.
With the increasing volumes of healthcare data captured using cloud-based applications, AI would eventually become a fool-proof and scalable solution, covering the whole spectrum of clinical applications from prevention to diagnostics to treatment, as well as non-clinical applications like patient engagement, workflow process and claims processing.
Furthermore, AI in healthcare provides support to clinicians for predictive analytics in real-time and solves operational challenges across the hospital functions. It also saves staff time, reduces steps, and removes paper-based processes through automated data collection, analysis, reporting and communication.
Overall, AI adoption is estimated to increase in the future, with expected increase in the number of acquisitions related to AI in healthcare. The enhanced functionalities of AI will revolutionize the way healthcare organizations operate.
At Mindfields, we have been driving innovation and excellence by leveraging disruptive technologies to optimize business processes that enable our clients to 'Grow for tomorrow'.
To learn more about applications of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare and the technology landscape, download Mindfields’ AI in Healthcare report here.
Topic: Artificial Intelligence, HealthCare, Blog

